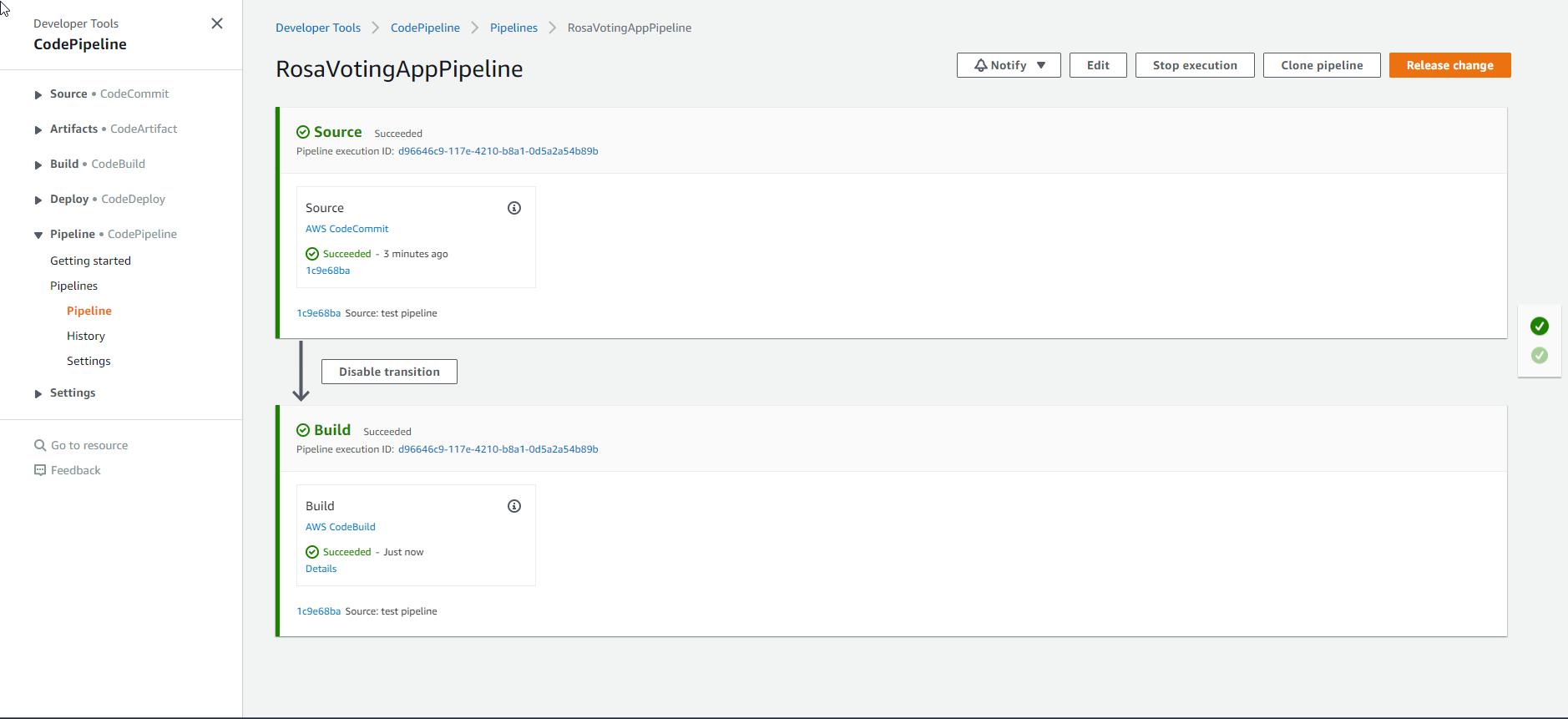
Set up CI/CD workflow for application deployment
Set up CI/CD workflow for application deployment
In this section, we will create a CI/CD flow to deploy the application to the ROSA cluster. We will reuse the components in the previous section (Basic CI/CD Workflow Setup) The architecture of the flow is as follows
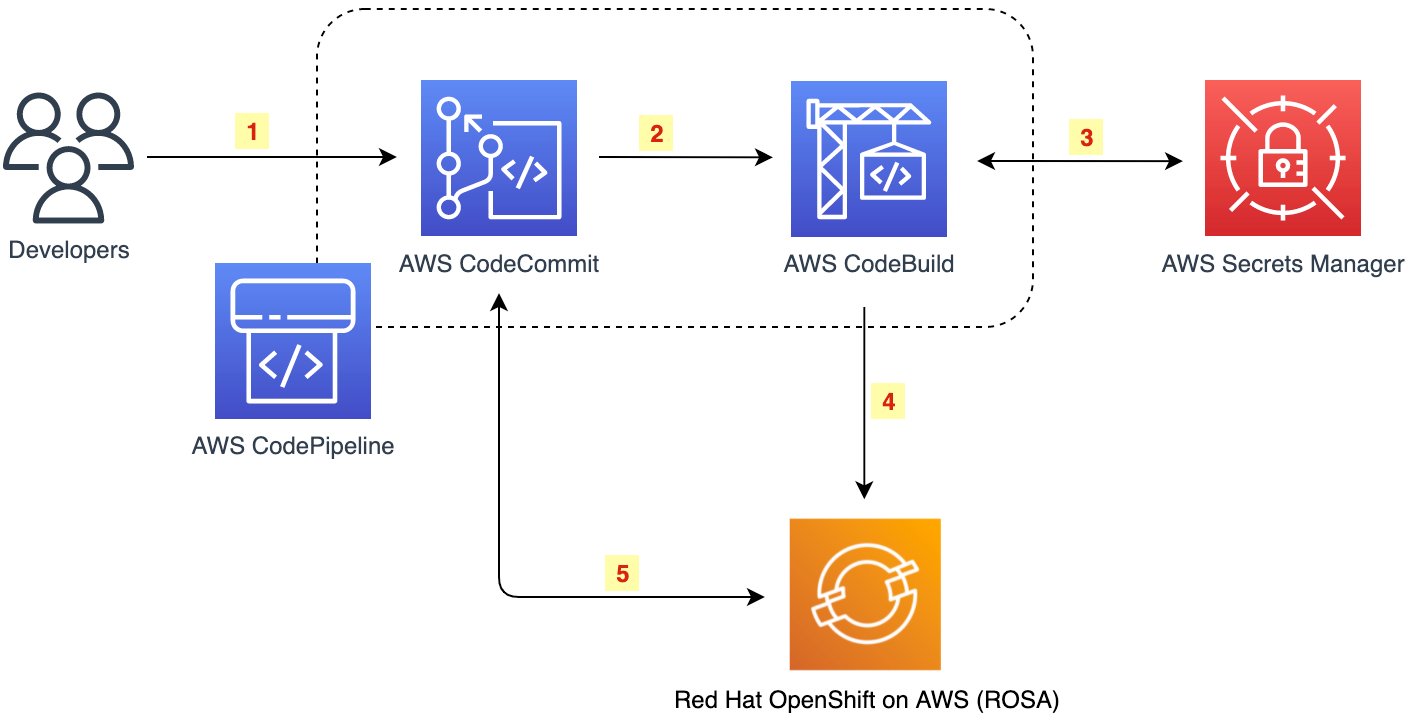
After the code is deployed to CodeCommit, CodeBuild will run and log into the ROSA cluster through the cluster credential values retrieved from ASM. ROSA will use S2I (source2image) to read the source code from CodeCommit, build the image, and push it to OpenShift’s local registry. The DeploymentConfig of the app deployed from the previous step will detect the change of the image through the ImageChange trigger and deploy a new application based on the updated image.
With CodeBuild, we have two approaches. First, CodeBuild can build the image and push it to the OpenShift registry, from which the corresponding Deployment will be activated and the application will be deployed. Second, CodeBuild can call the webhook of the OpenShift cluster, and OpenShift will use S2I to pull the source code from CodeCommit, inject the code, and build in a build container located on the OpenShift cluster. The final image will be pushed to the local registry and a new deployment will be deployed. In this lab, we will use the second method.
Configure CodeCommit secret
In order for OpenShift to communicate with CodeCommit, we will need to configure the CodeCommit secret, including the username and password to access CodeCommit.
-
Access to Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS
- Select Administrator
- Select Developer
-
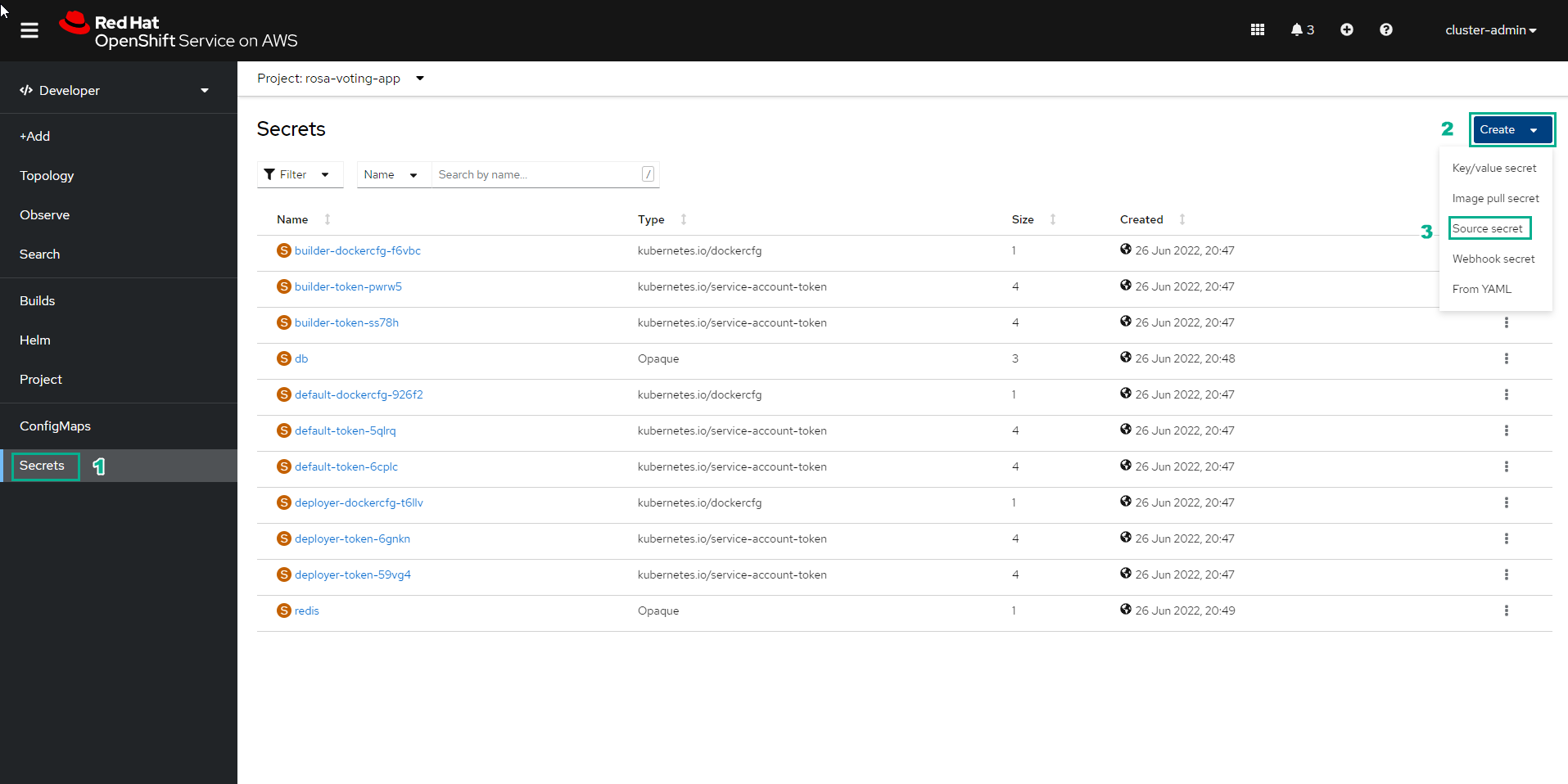
In the Secrets interface
- Select Create
- Select Source secret
-
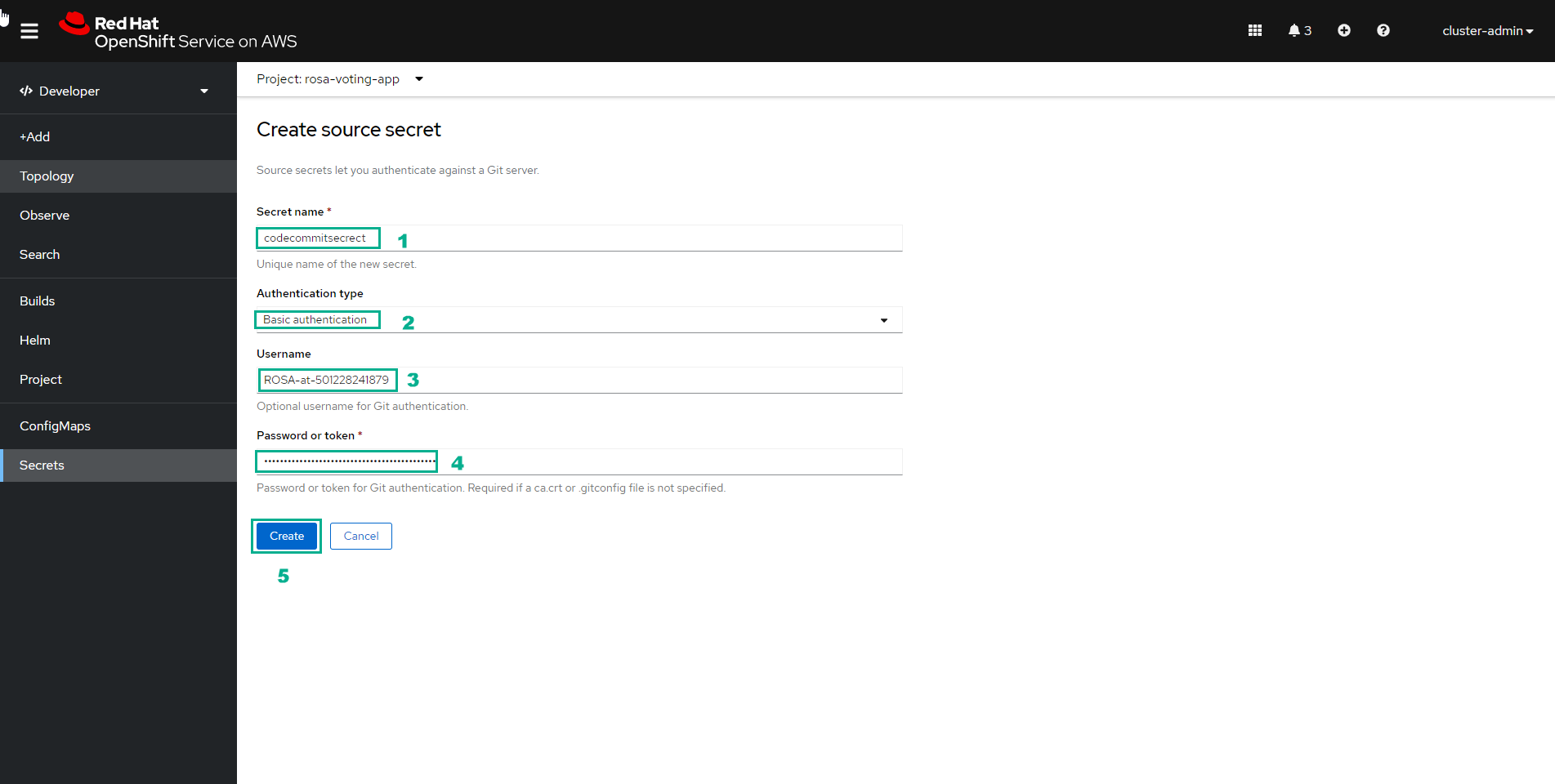
In the Create source secret interface
- Enter
codecommitsecretfor Secret name - Enter Username and Password or token
- Select Create
- Enter
-
Continue to select Secrets
- Select Create
- Select Webhook secret
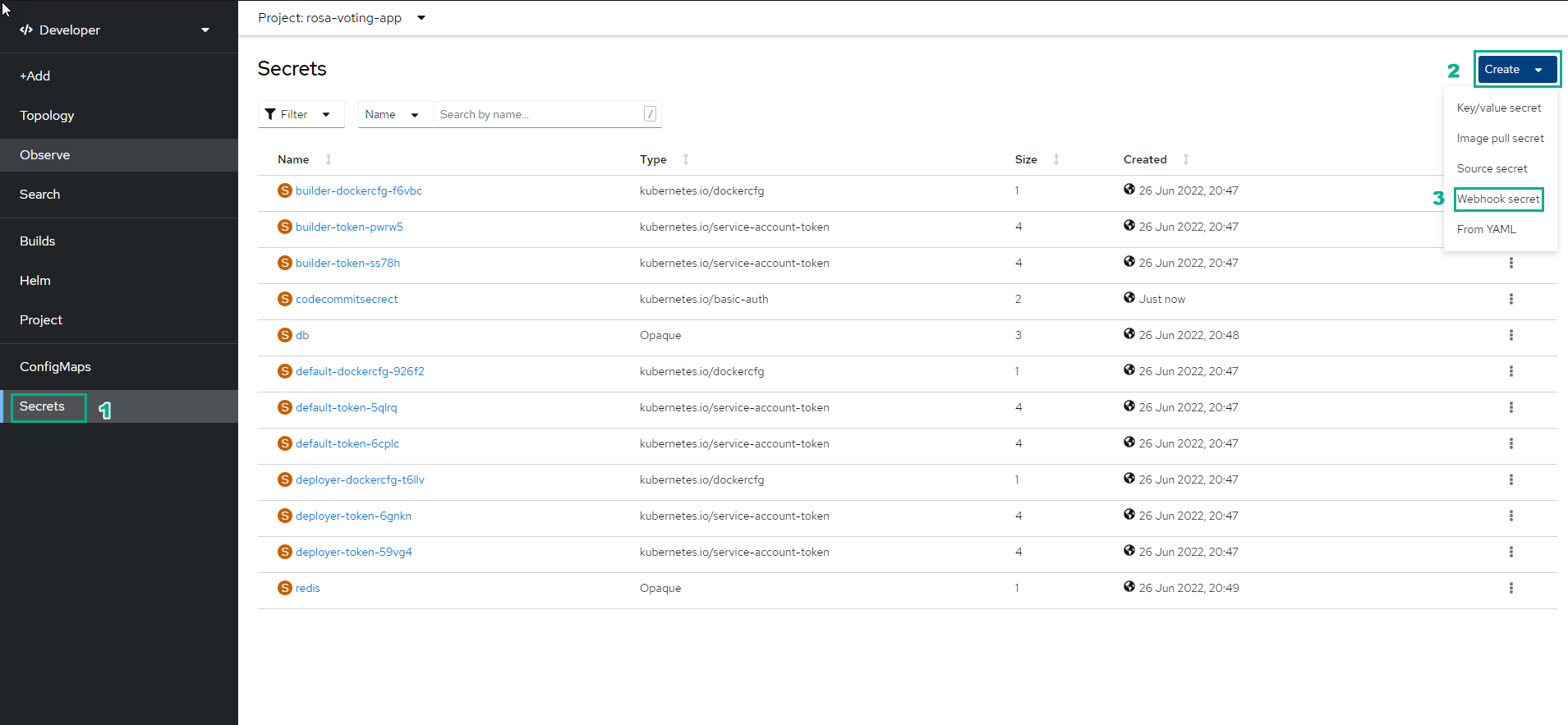
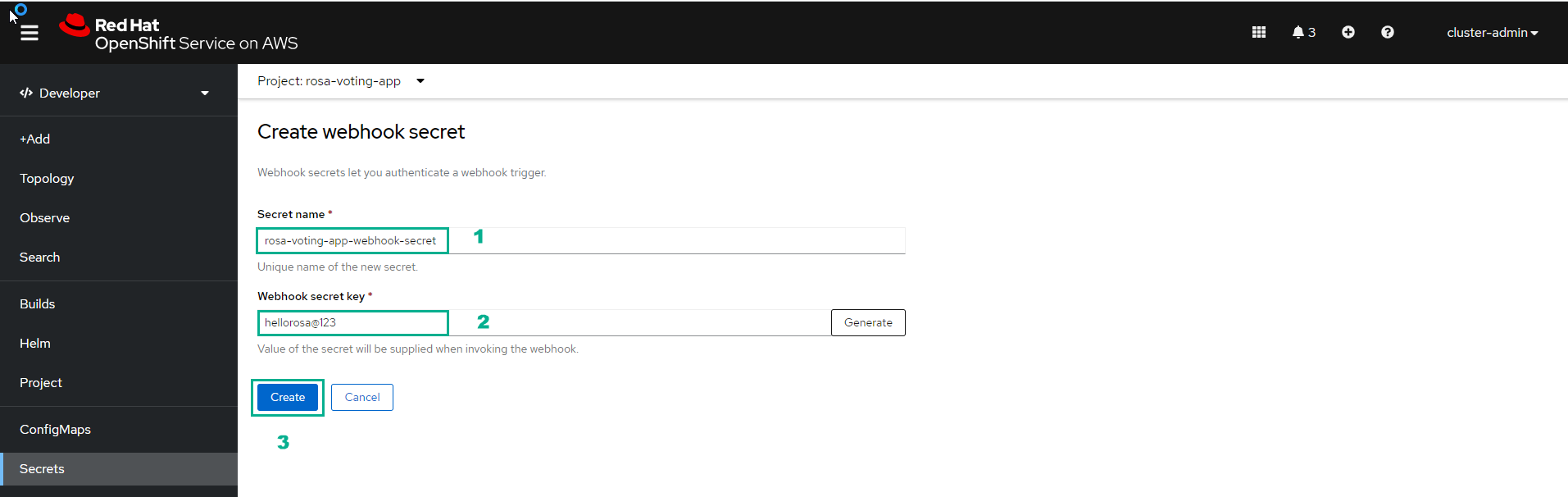
- Fill in the information and select Create*
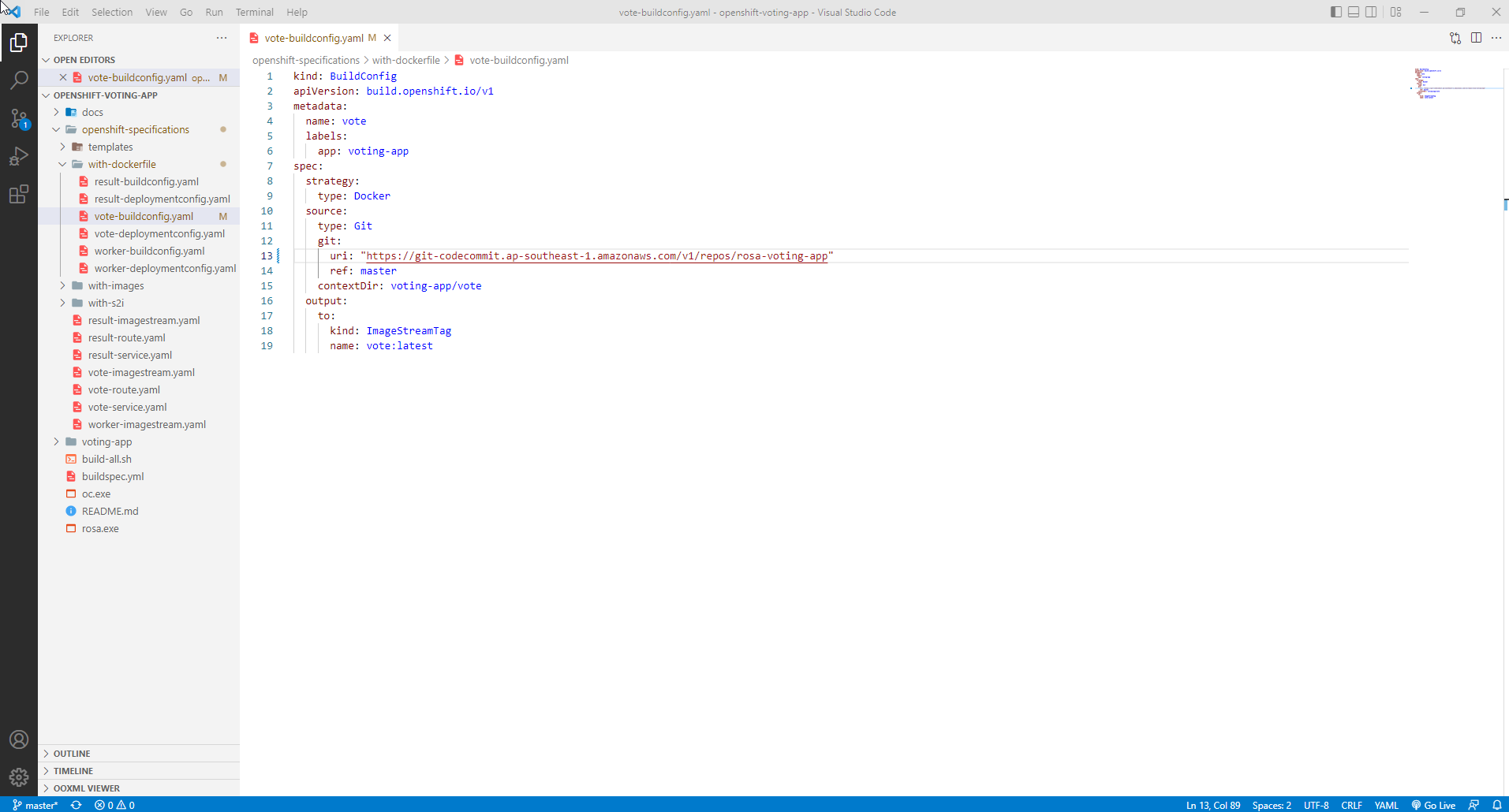
- Add secret information to config build yaml of app vote, change git url to url of CodeCommit repository
kind: BuildConfig
apiVersion: build.openshift.io/v1
metadata:
name: vote
labels:
app: voting-app
spec:
strategy:
type: Docker
source:
type: Git
git:
uri: "https://git-codecommit.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/v1/repos/rosa-voting-app"
ref: master
contextDir: voting-app/vote
sourceSecret:
name: codecommitsecret
output:
big:
kind: ImageStreamTag
name: vote:latest
Create a trigger for the webhook endpoint
- Add a trigger to the BuildConfig of the vote app to create a webhook endpoint. CodeBuild can use the generated endpoint to trigger the build event
kind: BuildConfig
apiVersion: build.openshift.io/v1
metadata:
name: vote
labels:
app: voting-app
spec:
triggers:
- type: Generic
generics:
secretReference:
name: rosa-voting-app-webhook-secret
key: WebHookSecretKey
strategy:
type: Docker
source:
type: Git
git:
uri: "https://git-codecommit.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/v1/repos/rosa-voting-app"
ref: master
contextDir: voting-app/vote
sourceSecret:
name: codecommitsecret
output:
big:
kind: ImageStreamTag
name: vote:latest
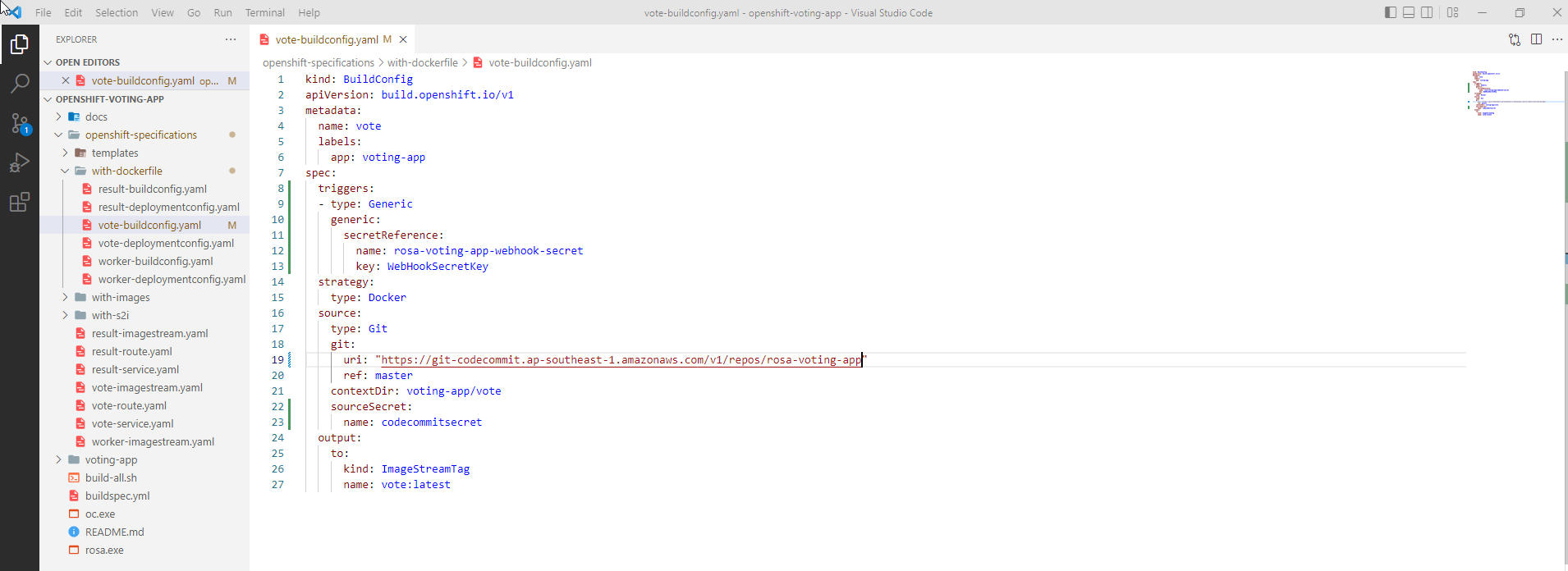
- Update BuildConfig
oc apply -f openshift-specifications/with-dockerfile/vote-buildconfig.yaml

Buildspec file configuration
-
Access AWS Secrets Manager
- Select Store a new secret
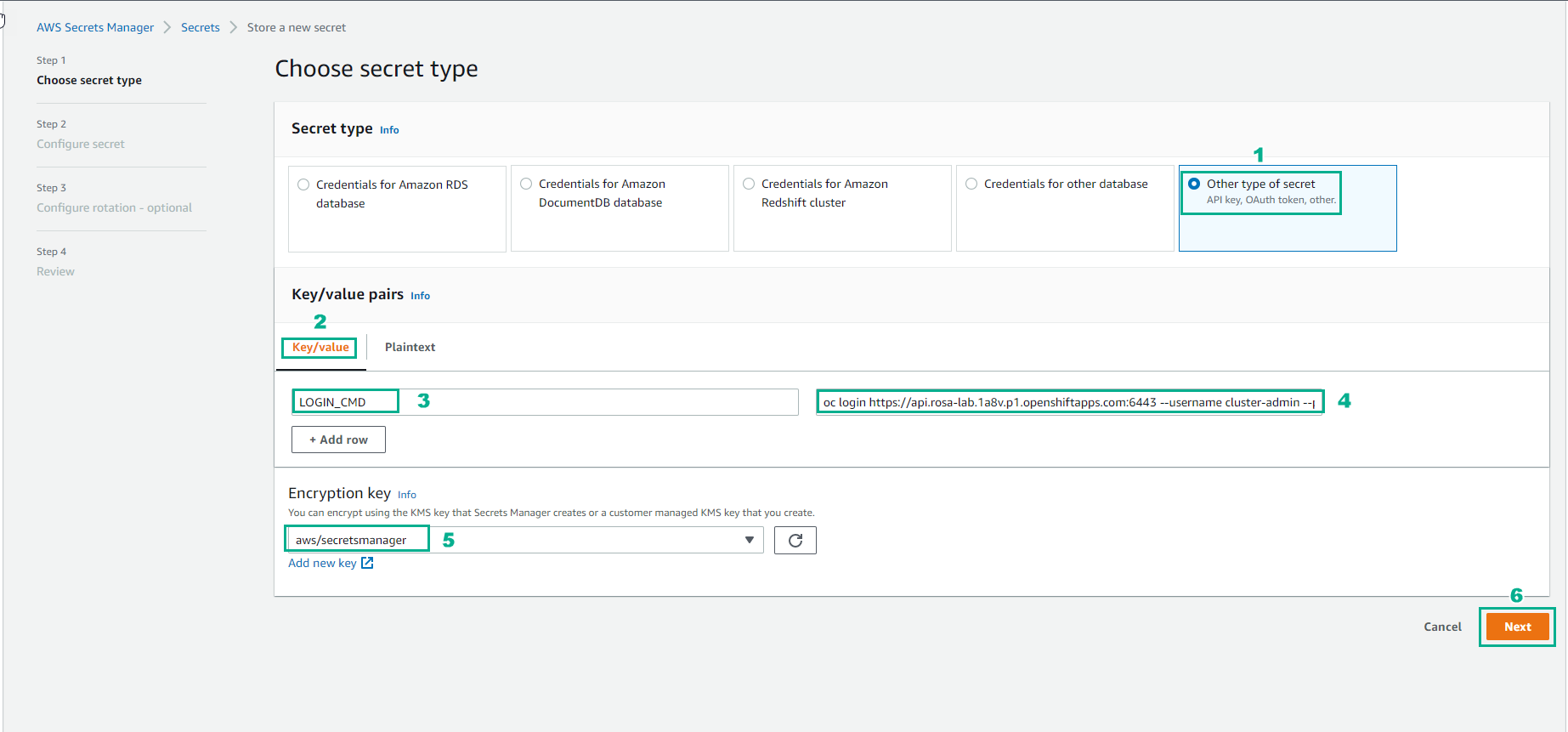
-
In AWS Secret Manager, create a new value containing the command to log into the OpenShift cluster. This information will be used in the build script
- Select Next
- Enter Secret name and select Next
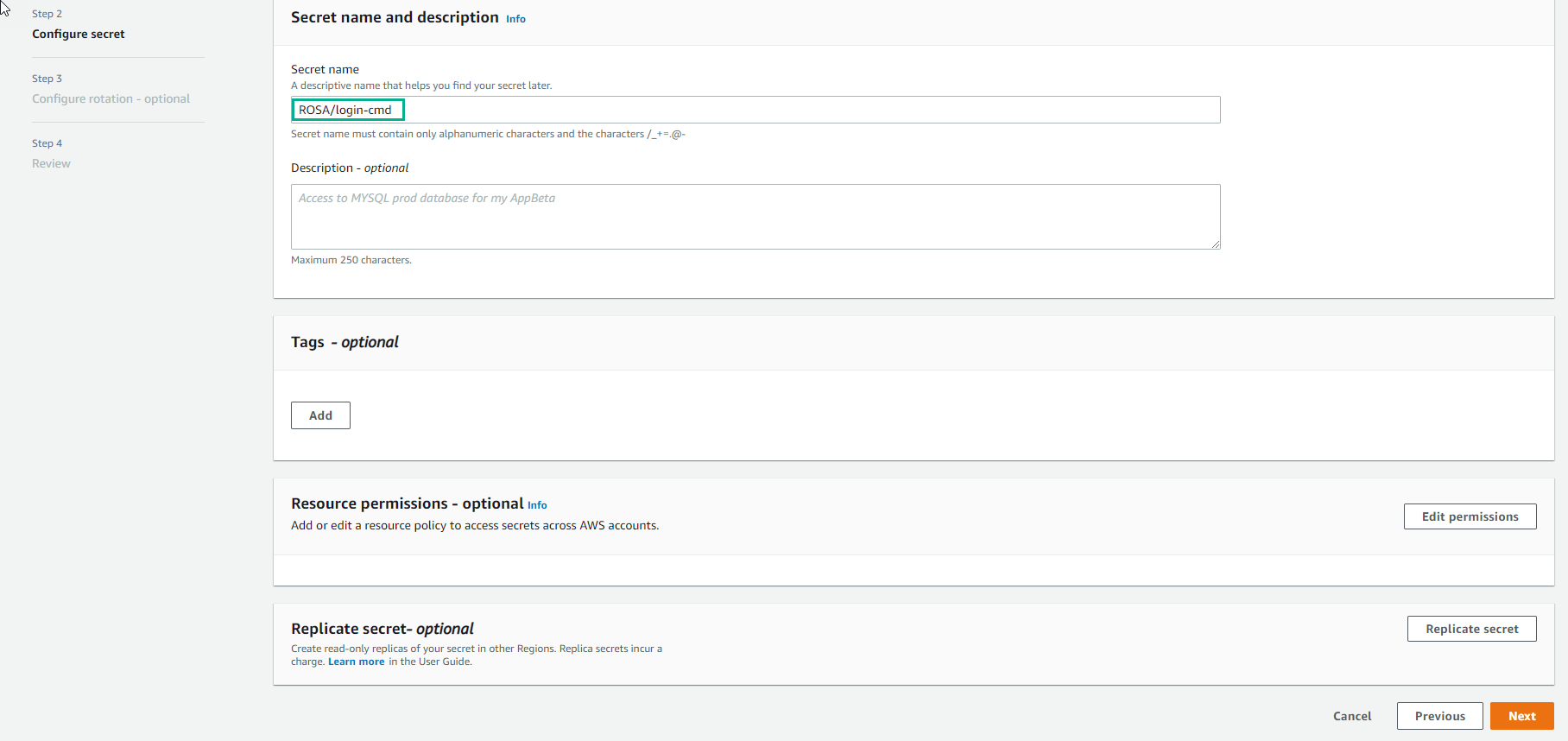
- Finish creating secret.
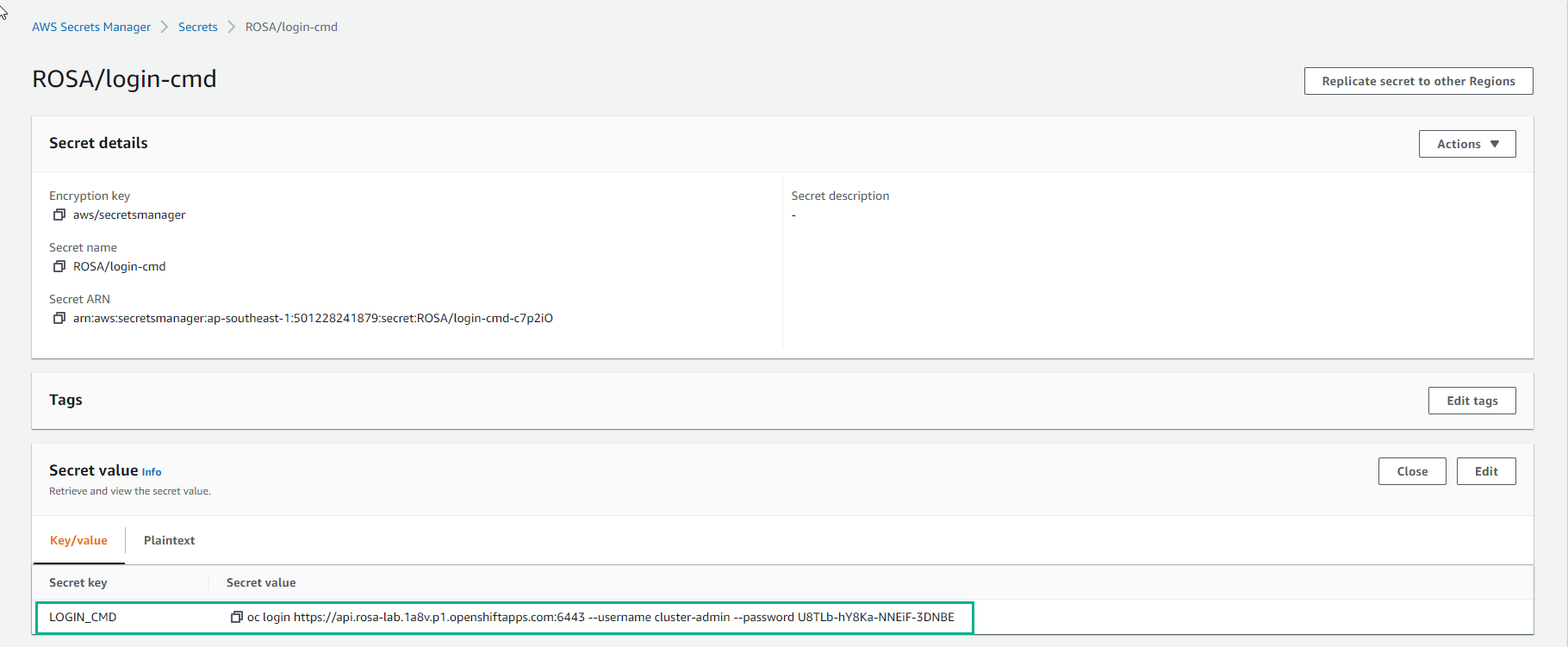
- Add SecretsManagerReadWrite policy for CodeBuild service role
- Select Attach policies
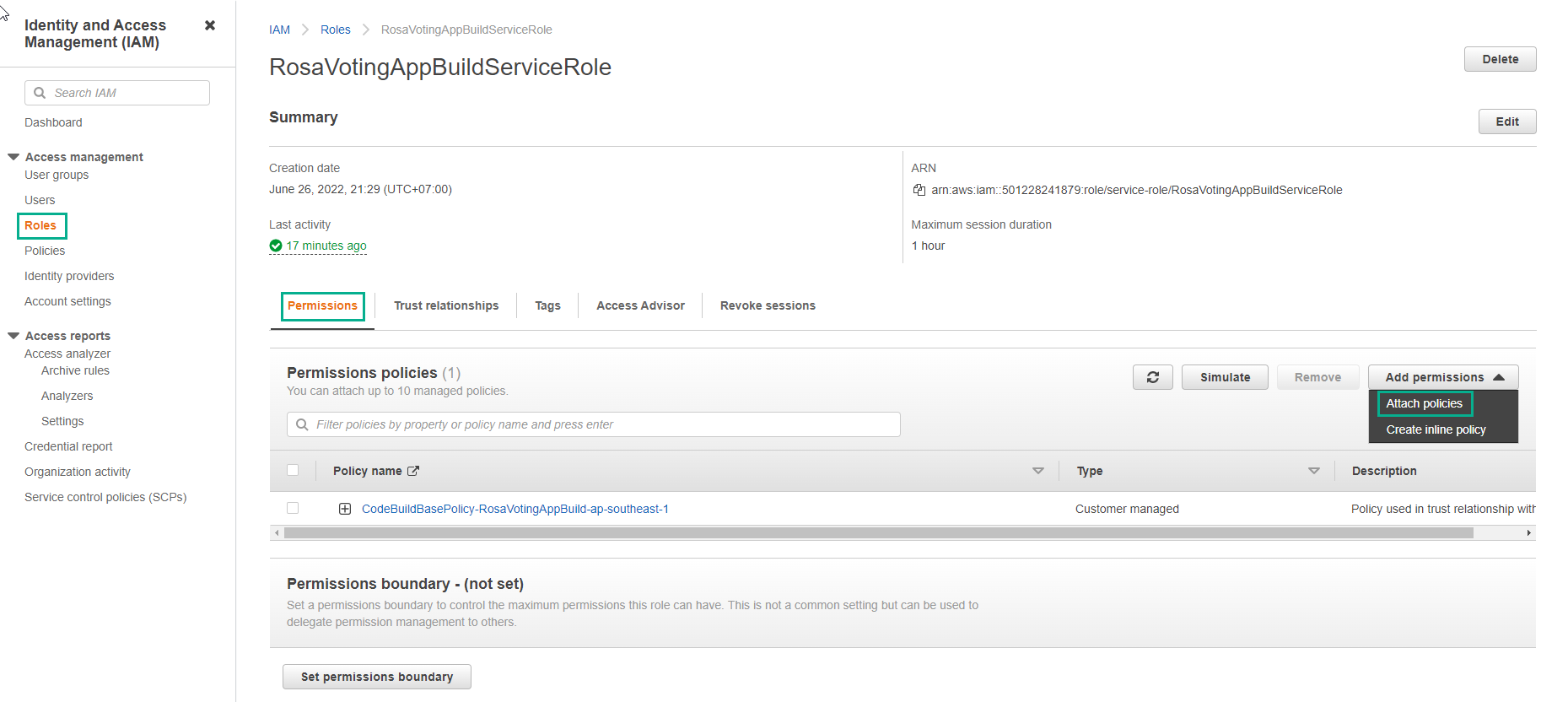
- Find and select SecretsManagerReadWrite
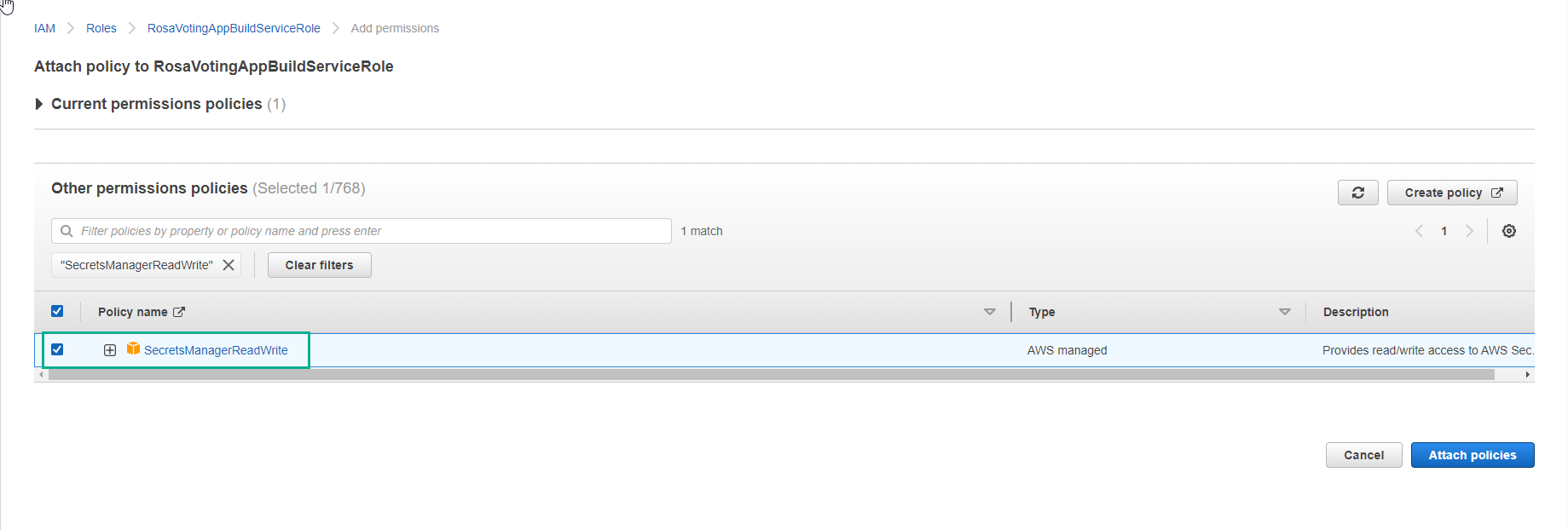
- Complete assignment of SecretsManagerReadWrite policy for CodeBuild service role
- Update buildspec to trigger webhook every time there is a code change
version: 0.2
phases:
pre_build:
commands:
- echo Hello World
- echo Testing codebuild flow
- apt-get install wget curl
- wget https://mirror.openshift.com/pub/openshift-v4/clients/ocp/latest/openshift-client-linux.tar.gz
- tar xzf openshift-client-linux.tar.gz
- cp oc /usr/local/bin
build:
commands:
- echo Building the 3 apps...
- bash build-all.sh # in project root dir
post_build:
commands:
- echo Test successful!
- echo Another pipeline has been triggered
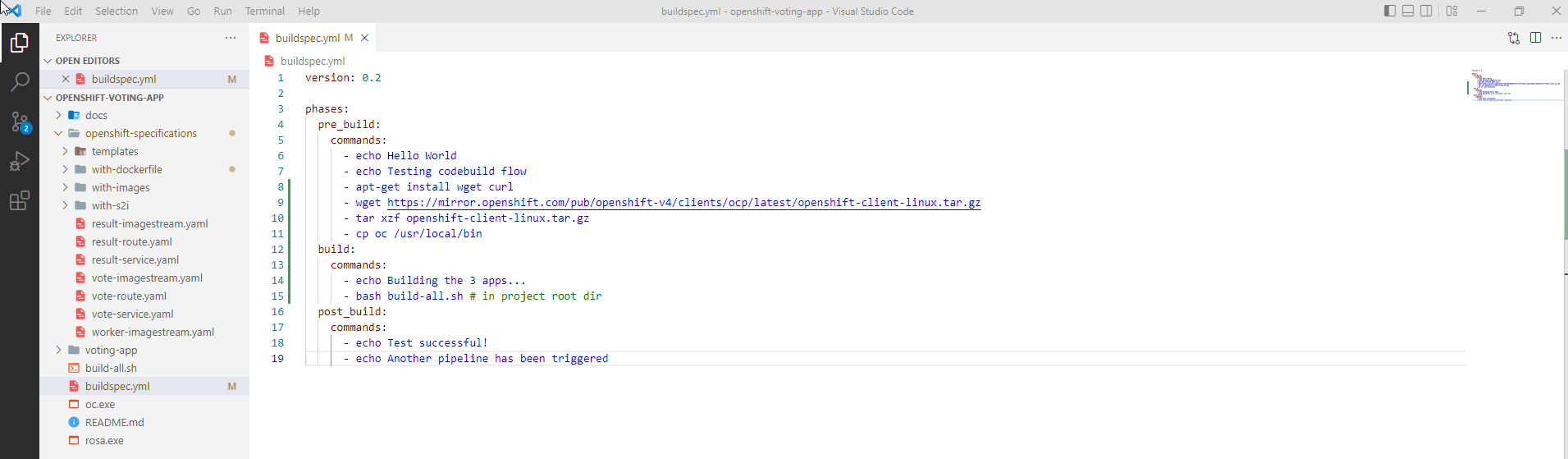
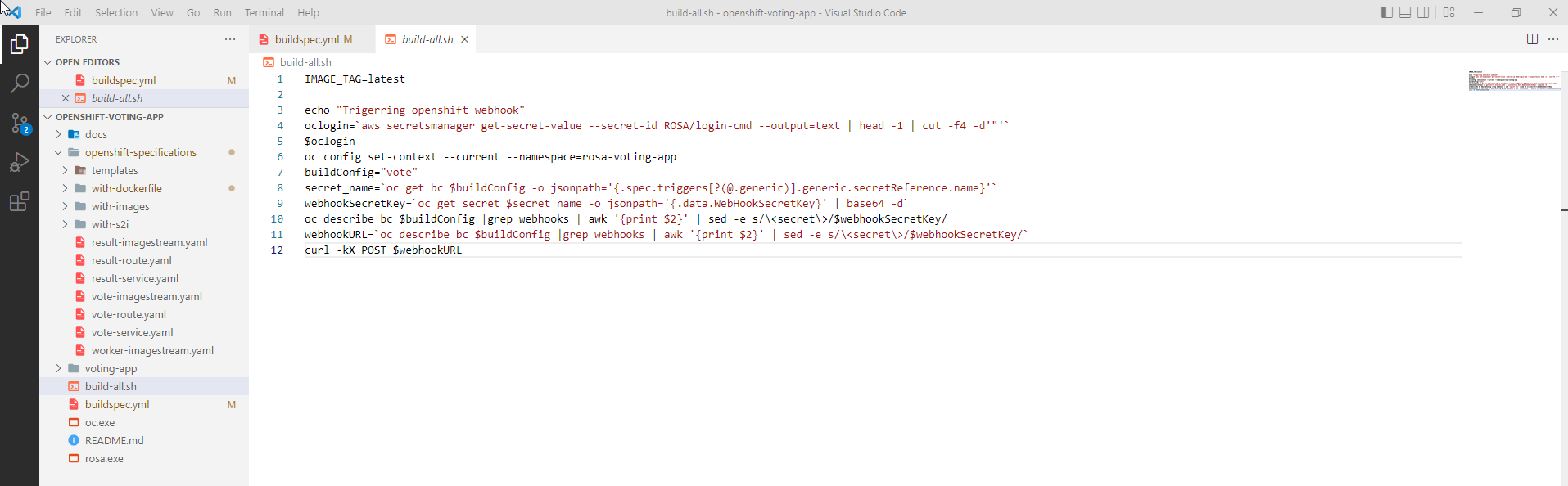
- The build-all.sh file has the following content
echo "Trigerring openshift webhook"
oclogin=`aws secretsmanager get-secret-value --secret-id ROSA/login-cmd --output=text | head -1 | cut -f4 -d'"'`
$ologin
oc config set-context --current --namespace=tungch-voting-app
buildConfig="vote"
secret_name=`oc get bc $buildConfig -o jsonpath='{.spec.triggers[?(@.generic)].generic.secretReference.name}'`
webhookSecretKey=`oc get secret $secret_name -o jsonpath='{.data.WebHookSecretKey}' | base64 -d`
oc describe bc $buildConfig |grep webhooks | awk '{print $2}' | sed -e s/\<secret\>/$webhookSecretKey/
webhookURL=`oc describe bc $buildConfig |grep webhooks | awk '{print $2}' | sed -e s/\<secret\>/$webhookSecretKey/`
curl -kX POST $webhookURL
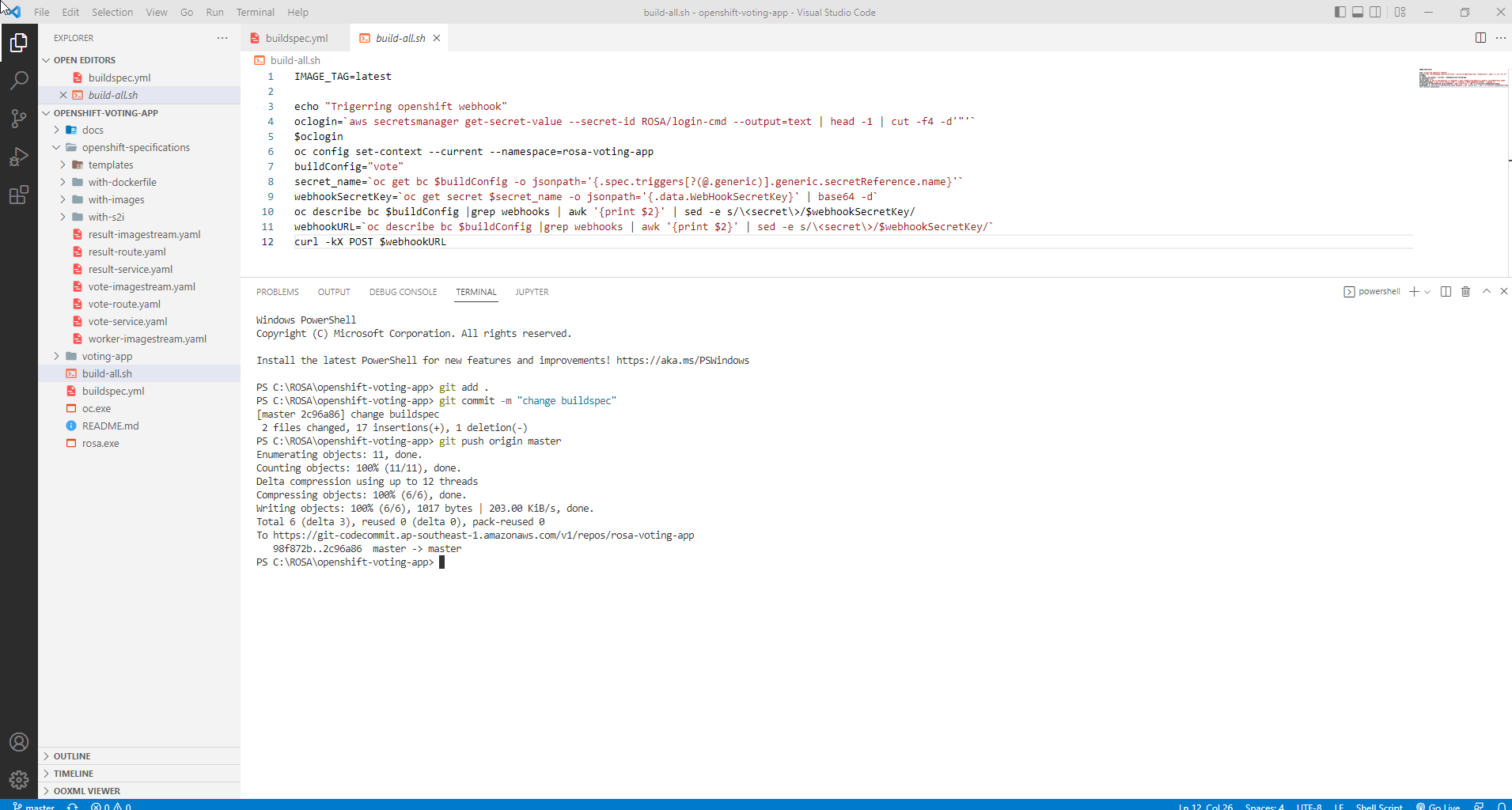
- Update code to CodeCommit
git add .
git commit -m "change buildspec"
git push
- View the log to see the details of the pipeline running.
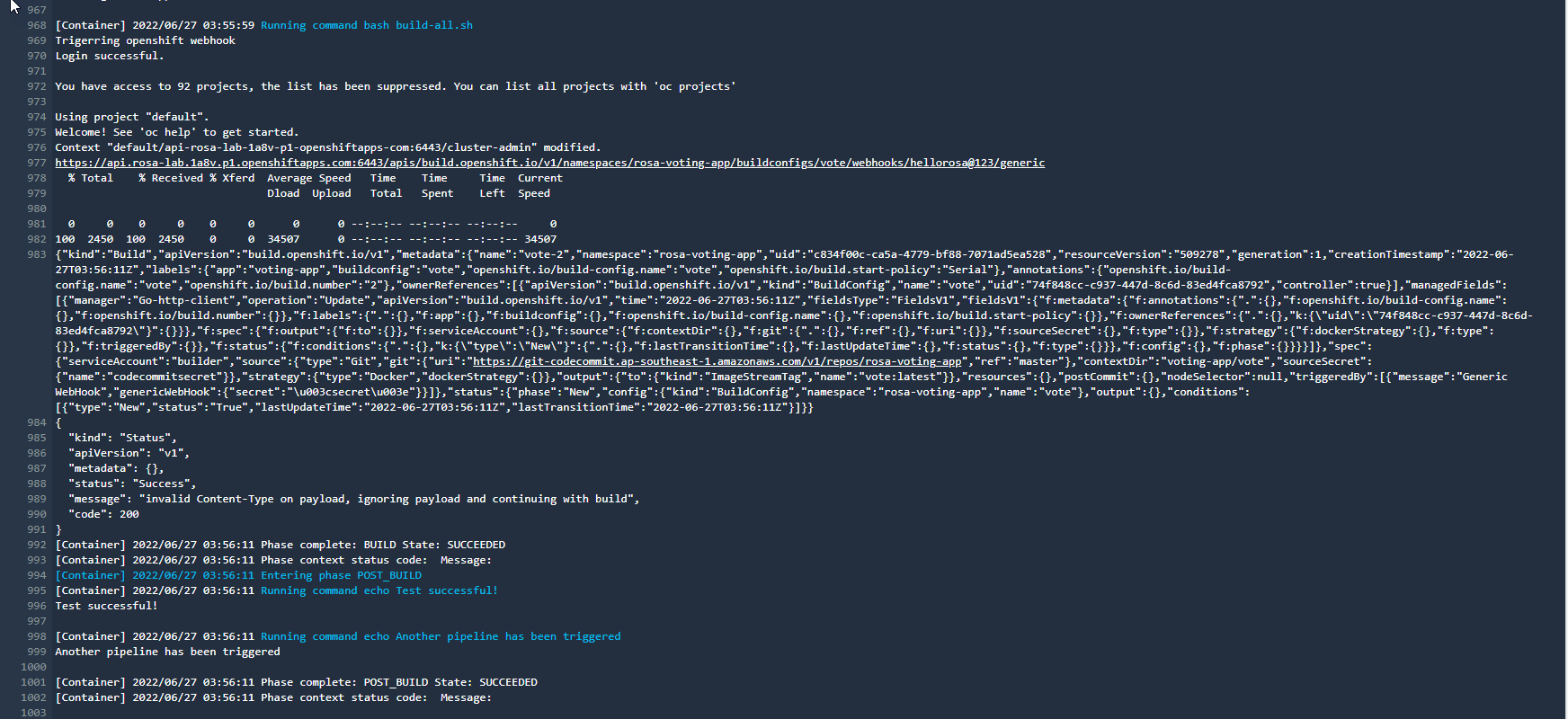
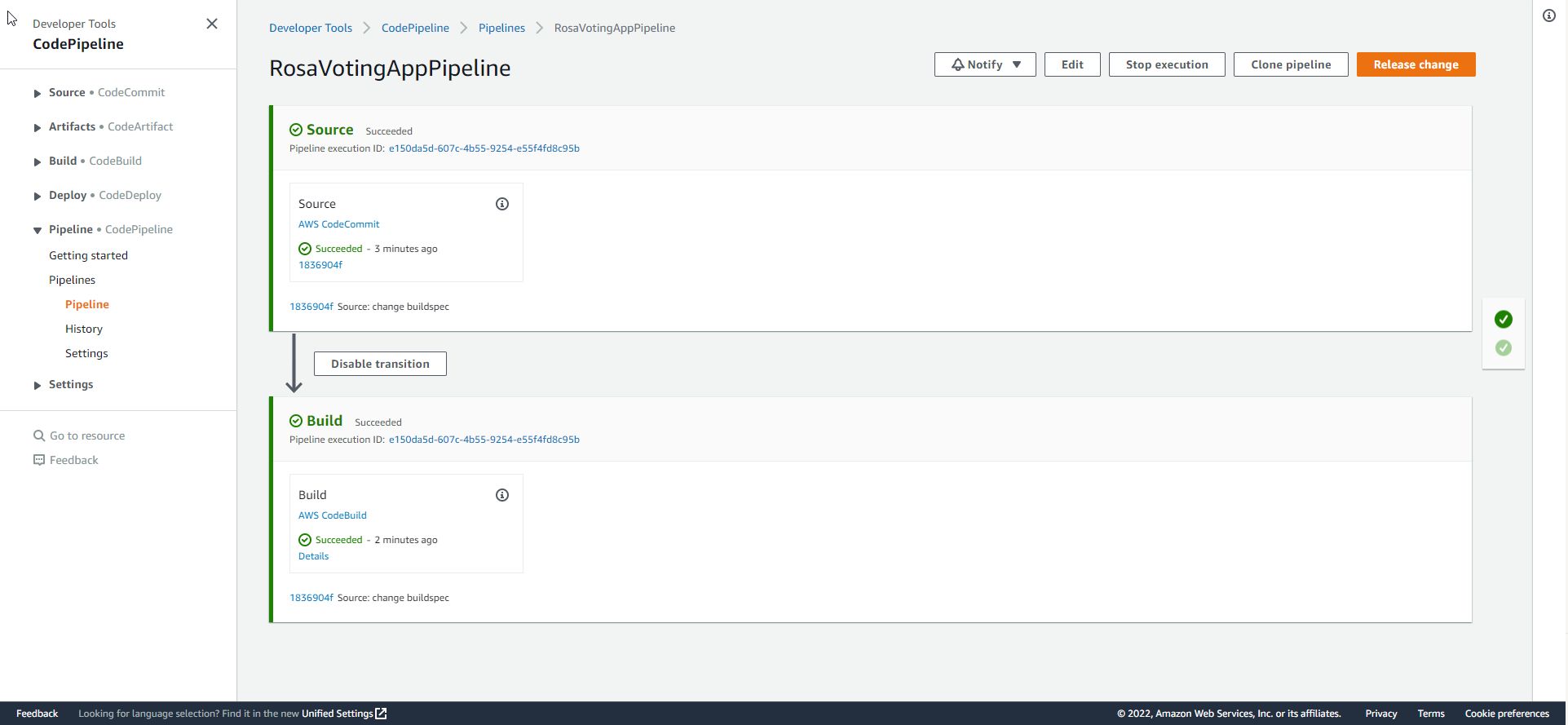
- Complete pipeline run. Thus, the CI/CD flow is complete. You can change the content of the vote app and the app will be deployed automatically.
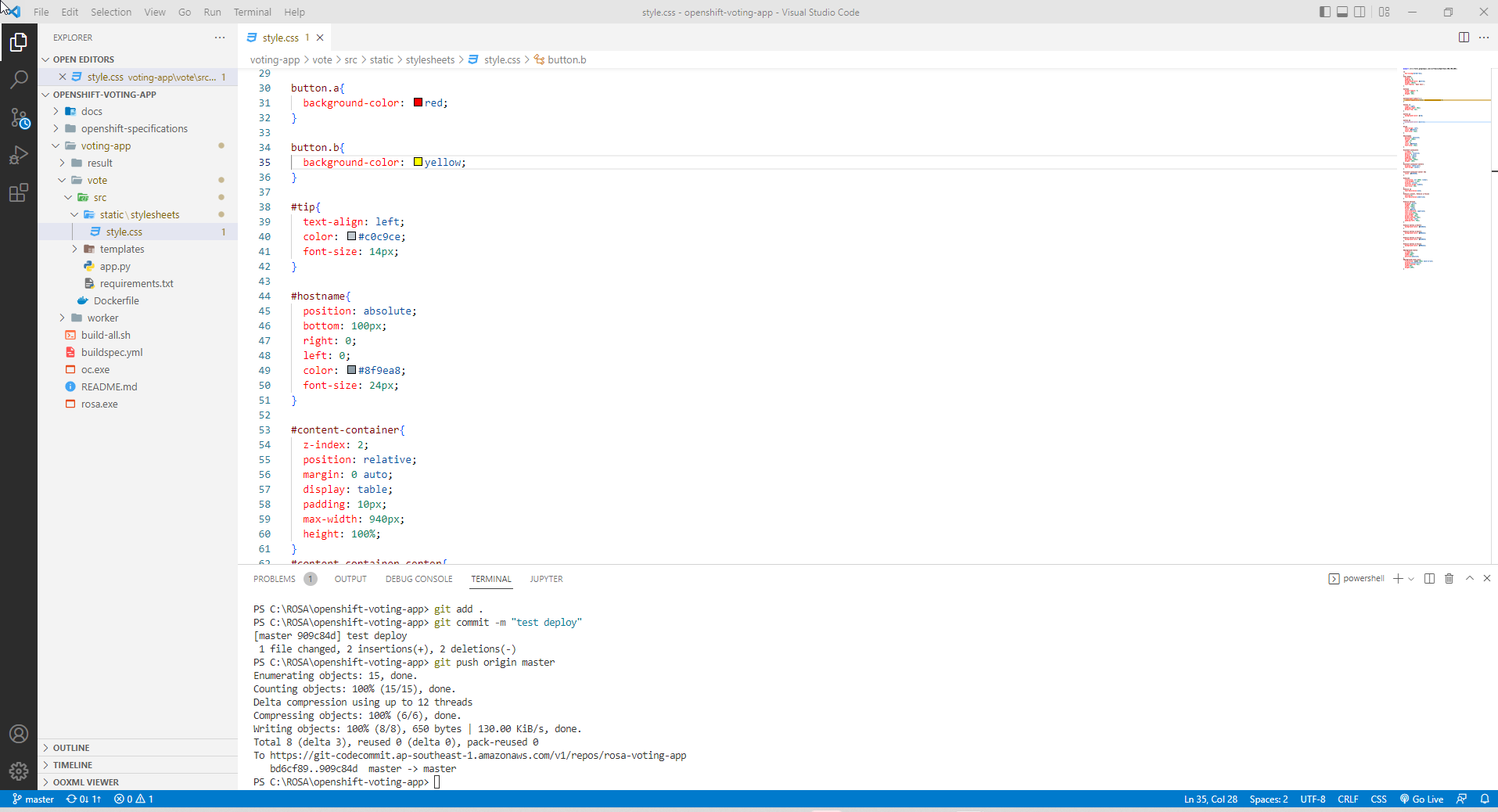
- Example of changing background color in voting-app/vote/src/static/stylesheets file:
- Complete test pipeline.